Quercetin Molecule - Health Benefits
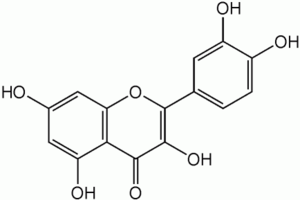
Quercetin is is a flavonoid, more specificlly a flavonol. Quercetin has a molecular mass 302.236 g/mol. It's molecular formula is C15H10O7
Health Benefits
Quercetin is one of the most active of the flavonoids. Many medicinal plants owe much of their activity to their high quercetin content. Quercetin has demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory activity because of direct inhibition of several initial processes of inflammation. For example, it inhibits both the manufacture and release of histamine and other allergic/inflammatory mediators. In addition, it exerts potent antioxidant activity and vitamin C-sparing action Quercetin also shows anti-tumour properties.
Food Sources of Quercetin
Foods rich in quercetin include capers (1800mg/kg), lovage (1700mg/kg, apples (440mg/kg), tea (Camellia sinensis), onions (higher concentrations of quercetin occur in the outermost rings, red grapes, citrus fruits, broccoli and other leafy green vegetables.
Drug Interactions
Quercetin is also a potent inhibitor of CYP3A4, an enzyme that breaks down most drugs in the body. As such, quercetin would be expected to increase serum levels, and therefore effects, of drugs metabolized by this enzyme.