Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG)
Epigallocatechin gallate, (EGCG) a catechin is considered to be a cancer chemopreventive in green tea. Catechins from green tea belong to the family of flavonoids that are powerful antioxidants and free iron scavengers.
IP-6
IP6( inositol polyphosphate), or phytic acid, is the principal storage form of phosphorus in many plant tissues, especially bran and seeds. It can be found in cereals and grains. In addition to reduction in cell proliferation, phytic acid increases differentiation of malignant cells often resulting in reversion to the normal phenotype
Glutathione
Glutathione is the most important antioxidant produced by the body. It prevents cellular damage caused by free radicals and peroxides.Glutathione is considered the master antioxidant and detoxifier found in every cell in your body.
Omega-3
Omega-3 fatty acids (omega-3s) have a carbon–carbon double bond located three carbons from the methyl end of the chain. ALA (shown above) is present in plant oils, such as flaxseed, soybean, and canola oils. DHA and EPA are present in fish, fish oils, and krill oils.
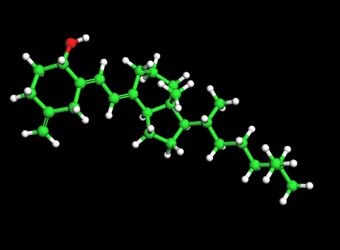
Vitamin D3
Vitamin D is critical for bone and muscle health, but it has recently been shown to be protective against acute respiratory infections
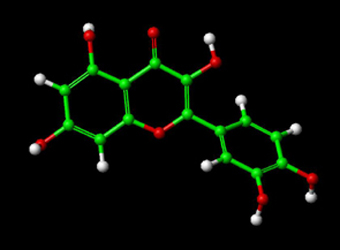
Quercetin
Quercetin belongs to a group of plant pigments called flavonoids found inmany fruits, flowers, and vegetables. Flavonoids, such as quercetin, are antioxidants.
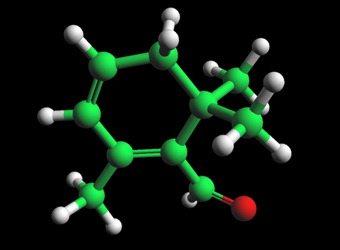
Safranal
Well known as a flavoring and odorant chemical, safranal is also known as an excellent antioxidant, and as a protective agent against indomethacin-induced gastric ulcers
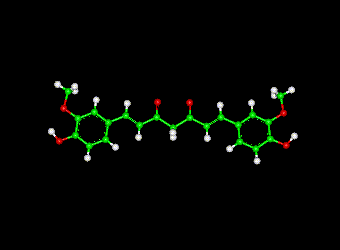
Curcumin
Curcumin is a yellow pigment that is a major component of turmeric and is commonly used as a spice and food-coloring agent. The past few decades have witnessed intense research devoted to the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin.
Capsaicin
Capsaicin stimulates the TRPV1 receptor. While capsaicin is not a cure for pain caused by these conditions, it does lower the amount of substance P, a chemical that helps transmit pain signals to the brain, when applied directly to the skinLatest News - Molecules in Health
A research study on 7,000 Italian men, combined with laboratory studies, confirms that drinking more than 3 Italian-style coffee cups a day reduces prostate cancer risk by more than 50 percent.Is it the Caffeine?. .. Read more
Glutathione, a molecule that was previously known only to eliminate harmful waste products of metabolism such as reactive oxygen species and free radicals. A team led by LIH researcher Prof Dirk Brenner, FNR ATTRACT fellow and Head of the Experimental & Molecular Immunology research group at the Department of Infection and Immunity, has discovered that glutathione also stimulates T cells' energy metabolism. .. Read more
Results suggest new directions for research on medications for heart conditions, pain relief and tissue growth
Results suggest new directions for research on medications for heart conditions, pain relief and tissue growth. Read more
As we grow old, our nights are frequently plagued by bouts of wakefulness, bathroom trips and other nuisances as we lose our ability to generate the deep, restorative slumber we enjoyed in youth. But does that mean older people just need less sleep? Read more
Urolithin A, a molecule found in pomegranates may improve muscle strength and endurance during aging
Capsaicin, an active ingredient of pungent substances such as chilli or pepper was shown to inhibit the growth of breast cancer cells...
Related Articles
- Towards a better screen: New molecules promise cheaper, more efficient OLED displays - August 8,2016
- Russian scientists speed up human tissue regeneration with supermolecule - August 6,2016
- Urolithin A Molecule --Pomegranate finally reveals its powerful anti-aging secret -- July 11, 2016
- First mirror image molecule spotted in interstellar space -- June 14, 2016
- Curry Derivative J147 Beats Aricept for Alzheimer's -- August 13, 2015
- Molecule based on structure of Curcumin fights Alzheimer's Diseas- January 21, 2015